
If you’re using the Carestream Exposure Index values, for every 300-exposure-index increase, the speed class is reduced by half. The exposure index is indirectly proportional to the speed class of operation. It’s the responsibility of the radiographer to select a technique that provides enough exposure to reduce the amount of noise while also adhering to ALARA standards.
Once an acceptable noise level is established, a radiographer can identify the speed class of operation for the imaging system and the corresponding technique charts. It’s important to note that, as speed class increases, so does the amount of image noise. The radiologist’s feedback on sample images helps determine the level of image noise he or she can accept. The speed class is set in a given department by consulting with an interpreting radiologist. The exposure index allows the radiographer to match the exposure to the desired speed class of operation. The number is a representation of the average pixel value for the image in a predefined Region of Interest (ROI). After an exposure is made, the resulting image appears on the monitor and displays a number in the Exposure Index field. The names include S-number, REG, IgM, ExI and Exposure Index.Ĭarestream’s computed radiography (CR) and digital radiography (DR) systems both reference their exposure indicator as the exposure index or EI. The exposure indicator has as many different names as there are vendors in the market. The indicator is a vendor-specific value that provides the radiographer with an indication of the accuracy of their exposure settings for a specific image (ASRT, 2010). An over- or under-exposed image will deliver an incorrect exposure indicator whereas a correct exposure will provide a corresponding exposure indicator. On digital imaging systems, an exposure indicator provides useful feedback to the radiographer about exposures delivered to the image receptor (ASRT, 2010). Read the related blog on Diagnostic Reference Levels.
UNDER EXPOSURE X RAY HOW TO
That’s why it’s so important for the radiographer to understand how to read and utilize the exposure indicators. The reason for this increased risk is that we’ve lost the visual connection between the exposure and an image’s appearance.

The potential for gross overexposure is one issue we encounter when a radiology department or clinic changes to a digital image receptor. So how does a radiographer know if a digital image is over- or under-exposed?

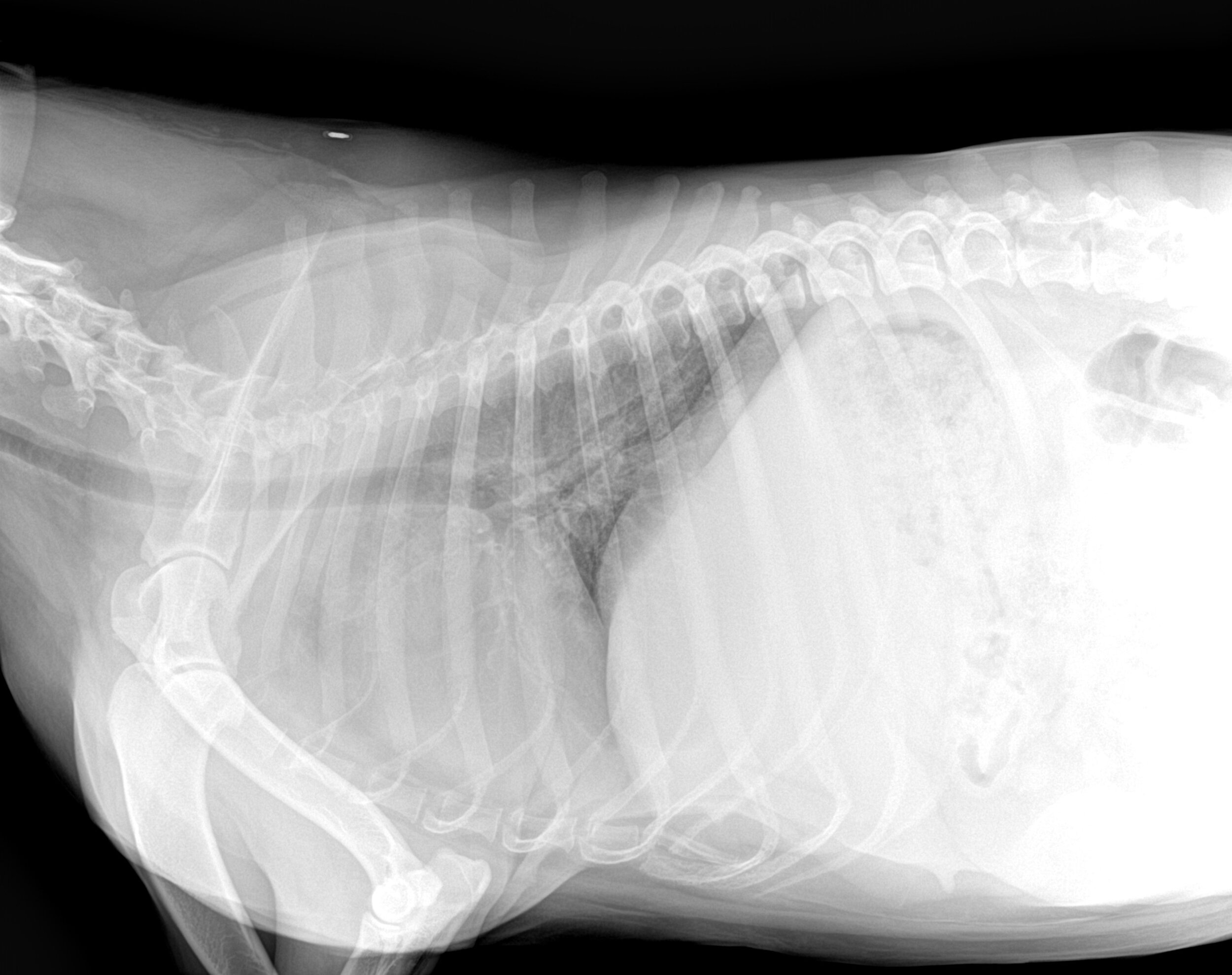
Digital systems produce images with consistent density and contrast regardless of the exposure factors (See figure 2).

However, with digital imaging devices, brightness and contrast are no longer linked to exposure factors. The density and contrast of the image on film is controlled by the kV, mAs and other exposure factors. You take your image, hold it up to the viewbox and say: “This image is too light” “This image is too dark” or, “This image is just right!” If you underexpose your image, it will be too light, and if you overexpose the image, it will be too dark (See figure 1). Imaging in a radiology film environment is much like playing Goldilocks and the Three Bears. Reading Time: 5 minutes read Knowing how number is used is key to controlling exposure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
